Carta Ramalan 4D Mkt 4D Magnum Damacai Toto

The Carta Planbee plays a crucial role for lottery enthusiasts participating in popular games like Magnum 4D, Sports ...
Read more3 Important tips: Carta Ramalan 4D Mkt 4D Magnum Damacai Toto
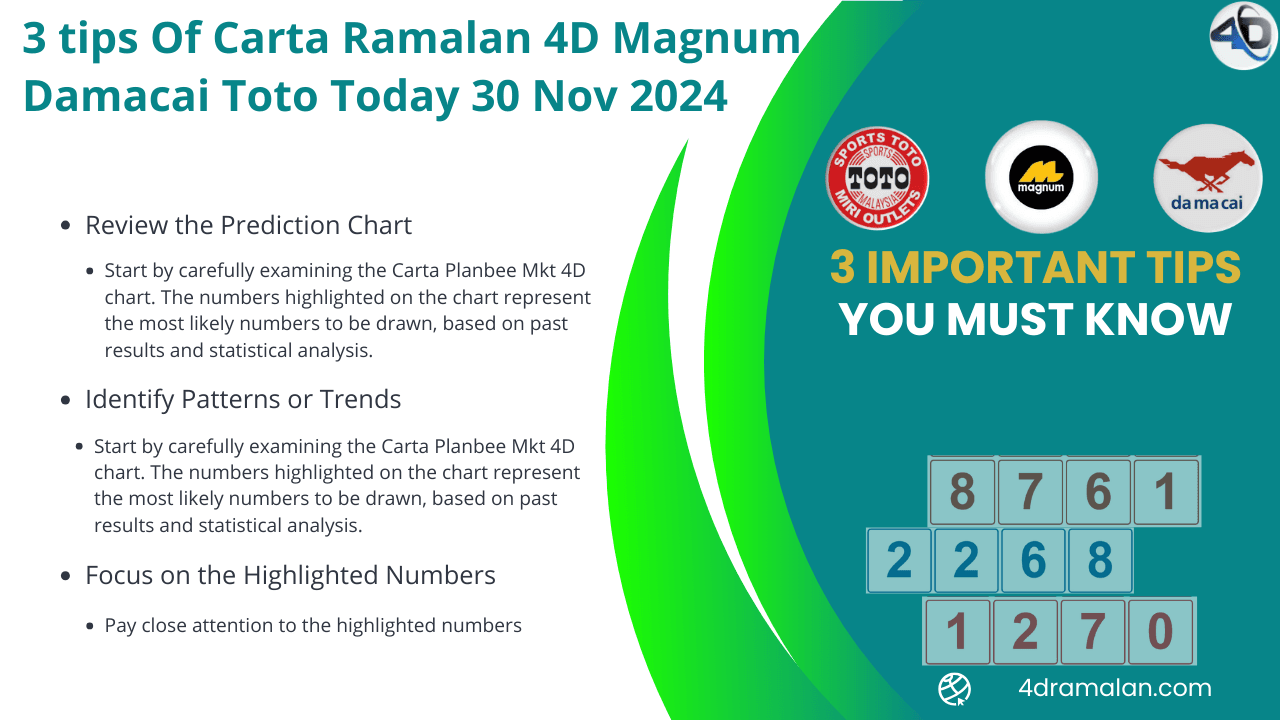
Mkt 4D has many secret tips, that everyone don't know. Carta Ramalan 4D shared secret tips to can help you win today's Magnum Damacai Toto.
Read more3 Important tips: Carta Ramalan 4D Mkt 4D Magnum Damacai Toto
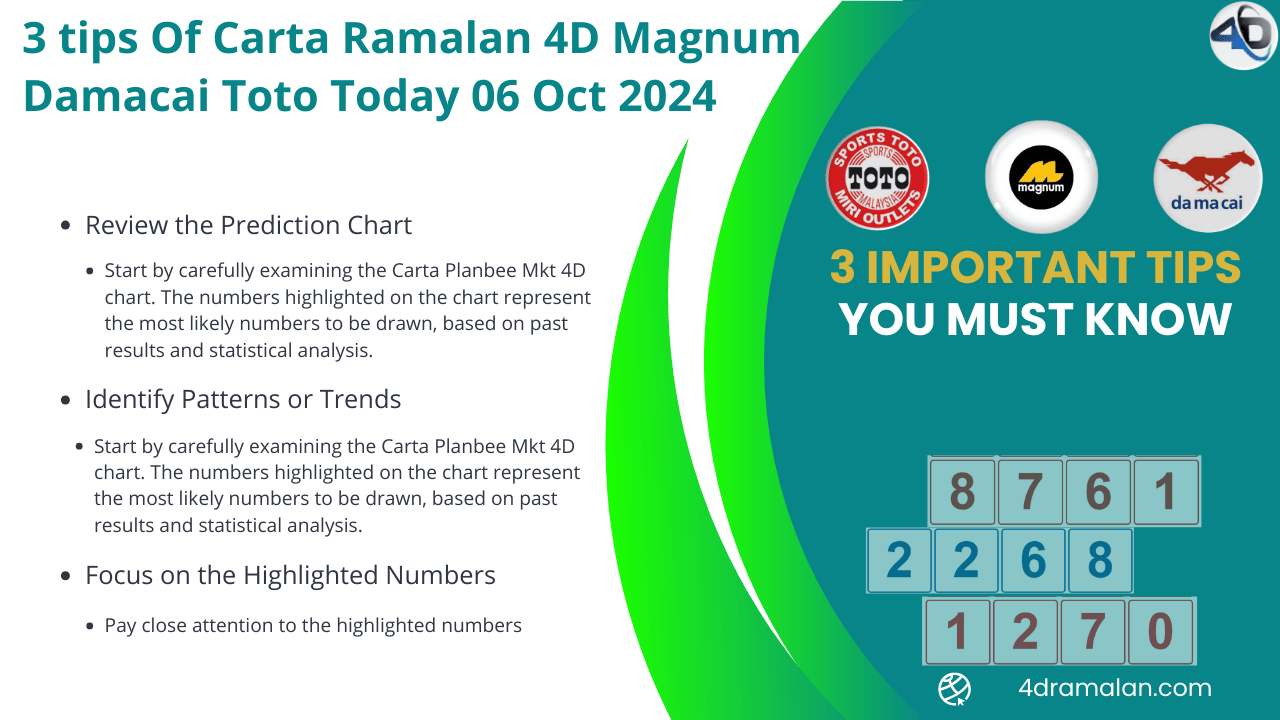
Mkt 4D has many secret tips, that everyone don't know. Carta Ramalan 4D shared secret tips to can help you win today's Magnum Damacai Toto.
Read more5 Important Tips: Carta Ramalan 4D Dragon 4D & Perdana 4D 06 Oct

5 Tip To Win Today Carta Ramalan 4D Gdl and Perdana 4D. This is an Amazing opportunity provided by 4D Ramalan to win today Dragon 4D Lotto.
Read more5 Tips To Win Today Carta Ramalan 4D 9 Lotto 4D 06 Oct 2024

Our team of lottery experts decoded the secret of 9 lotto 4d. At Carta Ramalan 4D we shared 5 important tips to win today 9 lotto 4d jackpot.
Read more3 important tips for Singapore Pools SGP 4D & SGP Toto 06 Oct

Carta Ramalan 4D announced most important tips about Singapore Pools, SGP 4D and SGP Toto, by following these tips you can win today jackpot.
Read more